Key Takeaways
- The suprachoroidal space is the potential space between the sclera and choroid layers of the eye.
- It allows drainage for glaucoma treatment and targeted drug delivery for retinal diseases.
- Suprachoroidal hemorrhage is bleeding into the suprachoroidal space, a serious complication.
- Understanding suprachoroidal anatomy aids glaucoma and retinal surgery outcomes.
- Research is advancing suprachoroidal drug delivery and retinal prosthesis implantation.
What is the suprachoroidal space??
The suprachoroidal space (SCS) is an important anatomical region of the eye located between the sclera and the choroid. But what exactly does “suprachoroidal” mean?
Supra- is a prefix meaning “above” or “over”, while the choroid is the vascular layer of the eye containing blood vessels that nourish the retina. So the suprachoroidal space refers to the potential space found above the choroid, between it and the fibrous outer layer of the eye called the sclera.
This narrow space is only about 20-60 microns wide but plays a crucial role in eye health and function. Understanding the anatomy and purpose of the suprachoroidal space is key for ophthalmologists and optometrists when diagnosing and treating various eye conditions.
What is the function of the suprachoroidal space??
The main functions of the suprachoroidal space involve:
- Drainage – The SCS facilitates drainage of fluid and blood from the interior of the eye. This is why it is targeted in glaucoma surgeries to lower inner eye pressure.
- Drug delivery – The space allows direct access for delivery of treatments to the choroid and retina, avoiding the blood-ocular barriers.
- Structural integrity – It provides a buffer zone between the vascular choroid and the fibrous sclera, along with anchorage points for the choroid.
- Passageway – The suprachoroidal space offers a pathway for nerves and blood vessels to connect with different eye structures.
- Surgical access – As a potential space, the SCS can be opened and accessed during ophthalmic procedures.
How is suprachoroidal anatomy relevant for eye surgery??
Understanding the precise anatomy of the suprachoroidal space has become increasingly relevant for eye surgeons. Advances in ophthalmic microsurgery have allowed new operative techniques targeting the SCS for treatment of conditions like glaucoma and retinal disorders.
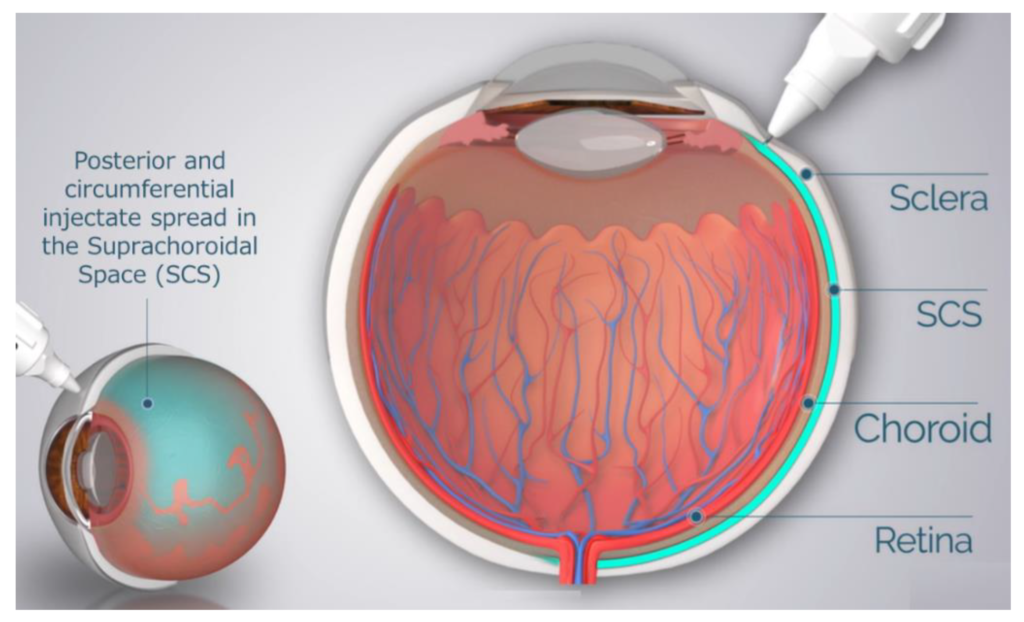
Some key ways suprachoroidal anatomy matters for surgery include:
- Allowing controlled drainage of fluid buildup inside the eye during glaucoma procedures.
- Providing a direct pathway for localized drug delivery to the posterior segment of the eye.
- Serving as an implantation site for retinal prosthetics to restore lost vision.
- Enabling minimally invasive procedures with faster recovery compared to traditional surgery.
- Reducing risk of complications by avoiding vital intraocular structures like the lens or retina.
- Optimizing outcomes by utilizing anatomical characteristics like the expansive surface area of the SCS.
Detailed knowledge of suprachoroidal space boundaries, nerve and vessel distribution, hydraulic conductivity, and other anatomical factors is crucial for surgeons to safely and effectively perform novel procedures targeting this region.
What is suprachoroidal hemorrhage??
While the suprachoroidal space facilitates eye health when functioning properly, it can also be the site of a severe ophthalmic complication known as suprachoroidal hemorrhage. This occurs when uncontrolled bleeding from the choroidal blood vessels accumulates within the suprachoroidal space.
Suprachoroidal hemorrhage is an emergency that causes a rapid rise in intraocular pressure, resulting in severe pain, blurred vision, nausea, and vomiting. Risk factors include hypertension, atherosclerosis, blood thinning medication, and intraocular surgery.
One study found the condition occurred in 0.2% of non-complicated cataract surgeries and up to 3.6% of complicated cases. Without prompt treatment, suprachoroidal hemorrhage can lead to permanent vision loss. Surgical drainage is required to remove the trapped blood from the suprachoroidal space and restore normal eye anatomy and pressure.
How are suprachoroidal injections used??
The suprachoroidal space has become an increasingly popular target for minimally invasive injection procedures to deliver ophthalmic drugs and gene therapies precisely where they are needed.
Medications injected into the SCS diffuse directly into the choroid and adjacent retina, reaching posterior eye structures without being diluted or broken down as occurs with intravitreal injections into the central cavity of the eye.
According to a 2022 study by Duke University, suprachoroidal injection benefits include:
- 3-4 fold higher drug concentrations in choroid and retina
- 50% lower required dosage compared to intravitreal injection
- Faster onset of action
- Longer duration of effect
- Reduced risk of complications
Suprachoroidal delivery is enabled by advanced microneedles that gently separate the sclera and choroid to access the narrow SCS. Drugs for treating retinal conditions like wet AMD and diabetic macular edema are being reformulated for off-label suprachoroidal use.
What is suprachoroidal buckling surgery??
Suprachoroidal buckling is a rare procedure performed for certain detachment cases where the retina becomes separated from the choroid and SCS. The surgery involves opening the SCS and inserting a silicone buckle to indent the wall of the eye from within the suprachoroidal space.
This narrows the SCS, bringing the detached retina back into contact with the choroid so it can reattach and heal. Studies show suprachoroidal buckling has a very high success rate for long-term retinal reattachment compared to other techniques.
Precise anatomical knowledge allows ophthalmic surgeons to safely perform this difficult procedure. The surgery requires meticulously constructing a periocular and suprachoroidal access tunnel to implant the custom-shaped buckle in the appropriate position within the SCS.
What is suprachoroidal retinal prosthesis implantation?
Retinal prostheses aim to restore vision to those with retinal degeneration by using electrodes to stimulate remaining healthy cells. The Argus II, approved in the US in 2013, is one epiretinal prosthesis that sits on the inner retinal surface.
An alternative approach currently in clinical trials uses the suprachoroidal space for prosthesis placement. Electrodes resting in the SCS are intended to more safely and effectively stimulate the choroid and adjacent retinal pigment epithelium.
According to a 2022 literature review, potential benefits include:
- Less retinal trauma during device implantation
- Enhanced device fixation and longevity of effect
- Lower surgical risk profile
- Improved biocompatibility and electrode conductivity
Meticulous understanding of suprachoroidal anatomy and dimensions allows precise surgical positioning of electrodes within the confined SCS to optimize visual signals.
What does the future hold for the suprachoroidal space?
From complex surgery to targeted drug delivery, the suprachoroidal space has proven its significance as an integral anatomical region and key target for ophthalmic therapies.
Continued research and advances in microsurgical techniques will further unlock its potential. Exciting possibilities on the horizon include:
- Novel glaucoma surgeries with ab interno suprachoroidal stents.
- Sustained-release drug formulations for suprachoroidal implants.
- Further development of suprachoroidal prosthesis technology.
- Use of suprachoroidal access to deploy retinal gene and stem cell therapies.
- Combination therapies merging drug delivery with implantable devices.
By leveraging unique anatomical advantages, the suprachoroidal space promises to play an expanding role in treating complex eye conditions and restoring vision. Ongoing discoveries will clarify remaining unknowns about SCS morphology, physiology, and surgical potential.
Conclusion
In summary, “suprachoroidal” refers to the potential space found between the fibrous sclera and the vascular choroid layers of the eye. Understanding suprachoroidal anatomy unlocks advanced surgical techniques and targeted drug delivery avenues that maximize the benefits of this narrow space, while avoiding risks like hemorrhage.
Continued research into optimizing suprachoroidal access and therapies will enable eye care professionals to harness the full potential of this intriguing posterior eye compartment for restoring sight
- Are Fructose and Glucose Isomers?
- Should You Have a Newline at the End of a File?
- Does Working Out Stunt Your Growth?
- Can Allergic Reactions Be Delayed?
- Does Intumescent Paint Need Primer?
- How to Unlock a Ford F250 Without Keys?
- Is It Too Late to Prune Camellias?
- Who’s Newt Scamander in Harry Potter?
- How Many Jobs Are Available in Air Freight/Delivery Services?
- What Are the Baggiest Dickies?
- How Much Does It Cost to Paint a Miata?
- How to Fix Shoe Sole Coming Off?
- How to Track Snapchat IP?
- Are Opened Clams OK to Eat?
- Do the Denominators Have to Be the Same When Subtracting Fractions??