Key Takeaways about Reps in Weight Lifting:
- Reps refer to the number of times you lift and lower a weight during an exercise.
- They help you track how much work you do during strength training.
- Higher reps use lighter weights, lower reps use heavier weights.
- Each set is a group of reps before resting.
- Reps help build muscle strength and endurance.
What exactly are reps in weight lifting?
When you do exercises with weights like barbells or dumbbells, a rep is when you lift the weight up and bring it back down once. Reps stands for repetitions.
So if you curl a dumbbell up towards your shoulder and then lower it back down, that is one repetition or rep. When you lift weights, you count your reps to see how much work you are doing.
Reps are an important part of strength training routines. Tracking reps helps you progress and meet your fitness goals over time. But how many reps should you do? And how do they fit into weight lifting sets?
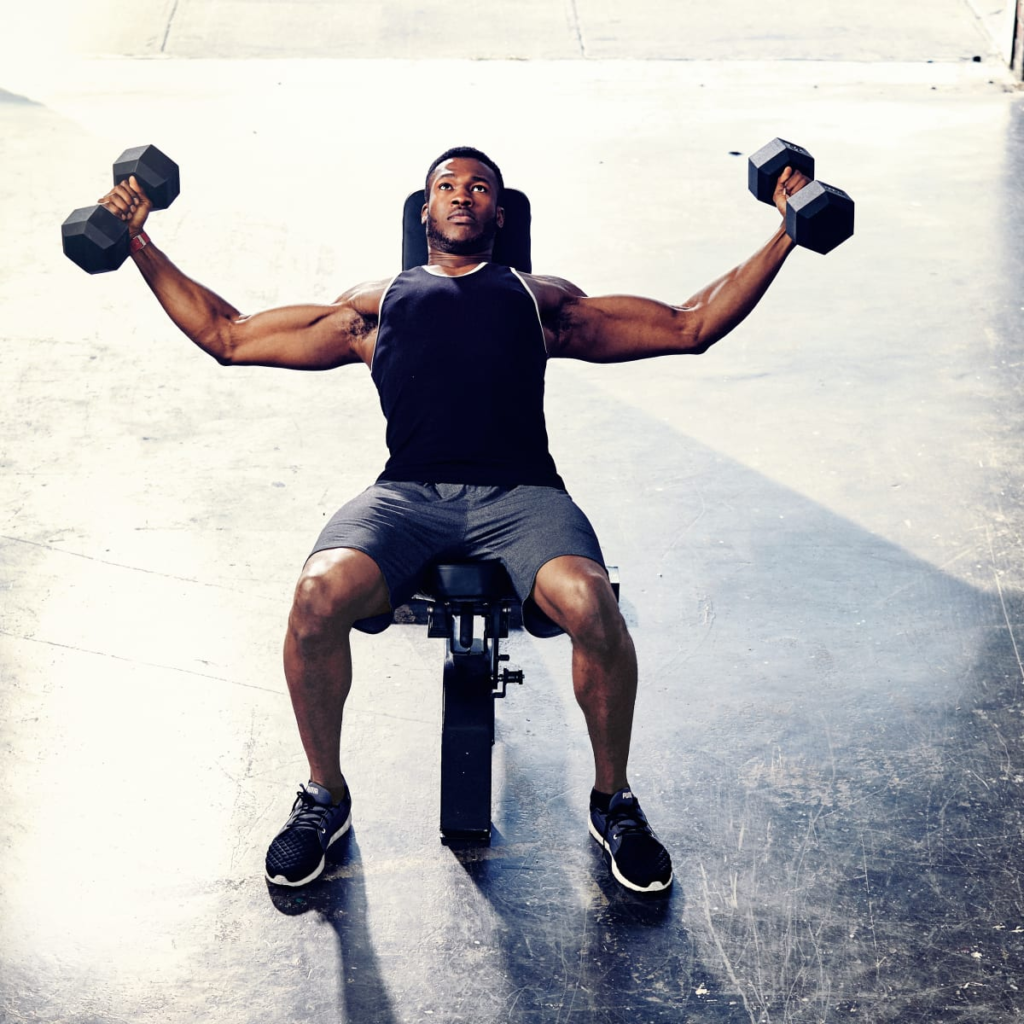

How many reps should you do per set?
The number of reps you do per set depends on:
- Your strength levels
- The amount of weight you are lifting
- Your goals – building muscle or endurance
As a general rule:
- Lighter weights = higher reps
- Heavier weights = lower reps
With lighter weights, you may do 15-20 reps per set. But with heavy weights, you may only do 6-8 reps per set before needing to rest.
Aim to lift weights that challenge you by the last 2-3 reps. If you can easily do extra reps with perfect form, go heavier. Proper form should come before hitting a rep target.

What are sets and how do they relate to reps?
When weight lifting, sets refer to groups of reps:
- A set is doing a number of consecutive reps before resting.
- Your rep goal counts for each set.
- Rest 1-3 minutes between sets to recover.
For example, 3 sets of 10 reps means:
- Lift the weight 10 times = 1 set
- Rest for 1-3 minutes
- Lift it 10 times again = 2nd set
- Rest again
- Lift it a final 10 times = 3rd set
So you complete 30 total reps over 3 sets. This builds muscle strength and endurance.
How do reps help build muscle?
Higher reps with moderate weight build muscle endurance. This increases stamina so you can lift for longer.
Lower reps with heavier weight build muscle size and strength. This allows you to lift more.
Varying rep ranges targets different goals:
- 8-12 reps build a mix of strength and muscle size.
- 6-8 reps build maximum strength.
- 12-15+ reps build muscular endurance.
Keep rep ranges in the 8-15 range for well-rounded muscle growth for most exercises. Go heavier for compound lifts like squats and deadlifts.
What rep speed should you use?
Control the weight up and down through the full range of motion. Avoid jerky momentum:
- 2 second count lifting the weight
- 1 second hold/squeeze at the top
- 2 second count lowering the weight
Go slowly to maximize tension on the target muscles. This leads to more gains over time. Momentum decreases the work your muscles do.
How do reps differ by goals like building muscle vs endurance?
Building muscle:
- Use heavier weights – about 70% of your max
- Do lower reps – 6-12 per set
- 2-5 sets per exercise
- Longer rests between sets – 2-3 minutes
Building muscle endurance:
- Use lighter weights – about 30-50% of your max
- Do higher reps – 12-20 per set
- 2-4 sets per exercise
- Shorter rests between sets – 1-2 minutes
Higher reps with lighter weights boosts stamina so you can lift longer. Heavier weights overload muscles to spur growth. Vary rep ranges to build both strength and endurance.
How should you increase reps and weights over time?
Start with lighter weights and higher rep ranges when learning new exercises. Focus on perfect form.
Once you can hit the top end of a rep range with good form, increase the weight slightly. Then work back up to the higher rep range again.
For example, increase weights once you can complete:
- 3 sets of 15 reps → Increase weight → Work back up to 3 sets of 15 reps.
This progressive overload principle is key for building muscle over time. Gradually challenge yourself.
What are drop sets and how do they relate to reps?
Drop sets involve decreasing the weight and immediately doing more reps:
- Lift heaviest weight until muscle fatigue at 6-8 reps
- Quickly reduce weight by 10-20% without resting
- Lift for as many reps as possible to failure
- Repeat dropping weight and reps to failure
This intensifies effort by extending reps beyond normal capacity. It is very demanding! Save drop sets for finishing a muscle group.

How can you use reps to break through plateaus?
Plateaus happen when progress stalls because the body adapts to your current routine. Strategic changes to rep ranges help shock your body to start making gains again:
- Drop reps from 12 down to 8 temporarily to prioritize strength.
- Vary heavier and lighter days for the same exercises.
- Take weight off the bar and go for higher volume sets of 15-20 reps.
- Include intensity techniques like drop sets, supersets, pyramids, etc.
Play with different rep schemes to find new ways to challenge your muscles. Then progress will resume.
What are common mistakes people make with reps?
It is easy to make mistakes with reps that limit their effectiveness:
- Not using full range of motion – Complete each rep through the entire movement. Partial reps do not fully work the muscle.
- Rushing reps – Lift and lower weights slowly to maximize tension. Avoid jerking the weight.
- Poor form due to fatigue – Keep good form as the priority. Use lighter weight if needed to maintain proper technique for the target reps.
- Not changing programs – Mix up rep ranges so your body does not adapt to the same routine.
Focus on quality, controlled reps with good form for best results over time. Leave ego at the door.
How do you count reps correctly?
There are some best practices for counting reps:
- Count the number of times you lift the weight up as the rep.
- The lowering phase after lifting is not counted.
- Count reps out loud or have a partner help count.
- Include failed attempts where you couldn’t complete the entire rep.
- Only count reps done with proper form through the full movement.
Accurately tracking reps completed per set ensures you progressively overload correctly each workout.
Can you build muscle with only bodyweight reps?
Yes, you can build muscle effectively with bodyweight reps! Resistance training principles apply the same:
- Use challenging progressions – decline pushups vs regular pushups.
- Do higher volume – increase total reps or sets.
- Use slower tempos – 3 second lowering phase.
- Increase density – reduce rest between sets.
- Add weight – wear a backpack or vest.
Follow a bodyweight program with enough sets, reps and progressions to drive muscle growth. Compound moves like pushups and pullups are great.
How many reps should a beginner do?
Beginners should start with 12-15 reps per set with lighter weights to focus on:
- Learning proper exercise form
- Developing muscle mind-connection
- Gaining strength endurance
Build a base before increasing weight and decreasing reps. High reps with lighter loads reduces injury risk.
Prioritize quality, controlled reps over hitting a certain number, especially as you are learning. Leave 1-2 reps “in the tank” on first sets.
Can you do too many reps?
Yes, you can overdo reps, leading to excess fatigue and stress:
- Extremely high reps per set like 30-50 can be unnecessary for muscle growth.
- Total weekly sets for a muscle group should stay in the productive range – not too low or too high.
- Take sets to failure too frequently can prolong recovery.
Optimal rep ranges for muscle growth are usually considered 8-15 reps per set. But you still need to progress load over time for continued gains.
How can rest times between sets impact reps?
- Longer rests of 2-3 minutes allow you to lift heavier weights for lower rep sets.
- Shorter rests of 1-2 minutes create fatigue, making higher rep sets more challenging.
Adjust rest periods to align with your goals:
- Strength – Take longer rests for heavier sets.
- Muscular endurance – Take shorter rests for higher rep sets.
Rest only as needed between sets to hit the target reps. As you get stronger, reduce rest periods to increase difficulty.
What are supersets and how do they relate to reps?
Supersets involve doing two exercises back-to-back with no rest between them. This increases training density for greater gains:
Sample superset:
- 10 reps of dumbbell rows
- Immediately do 10 reps of bench press
- Rest 1-2 minutes
- Repeat for 3-5 supersets
Because you move right between exercises, you get more total reps completed in less time. This adds an intensity that helps shock the body out of plateaus.
Can you build muscle with reps using only body weight?
Yes, it is possible to build muscle effectively using only bodyweight reps! The same principles apply:
- Progressive overload – increase reps or exercise difficulty over time
- Train to muscle fatigue – high effort levels
- Use full range of motion – avoid partial reps
- Vary rep speeds – explode then slow negatives
- Allow enough recovery between training sessions
With enough sets, reps, and progressions, bodyweight training provides a challenging muscle-building stimulus. Exercises like pushups, pullups, and squats are great examples. Add weight as you advance.
What does rep range mean?
Your rep range is the target number of repetitions you complete per set of an exercise. For example:
- 3 sets of 6-8 reps – you do 6, 7, or 8 reps on each set
- 4 sets of 12-15 reps – you complete 12, 13, 14 or 15 reps on every set
Different rep ranges have different effects. Varying your rep ranges over time helps produce well-rounded muscle development.
Here are common rep ranges:
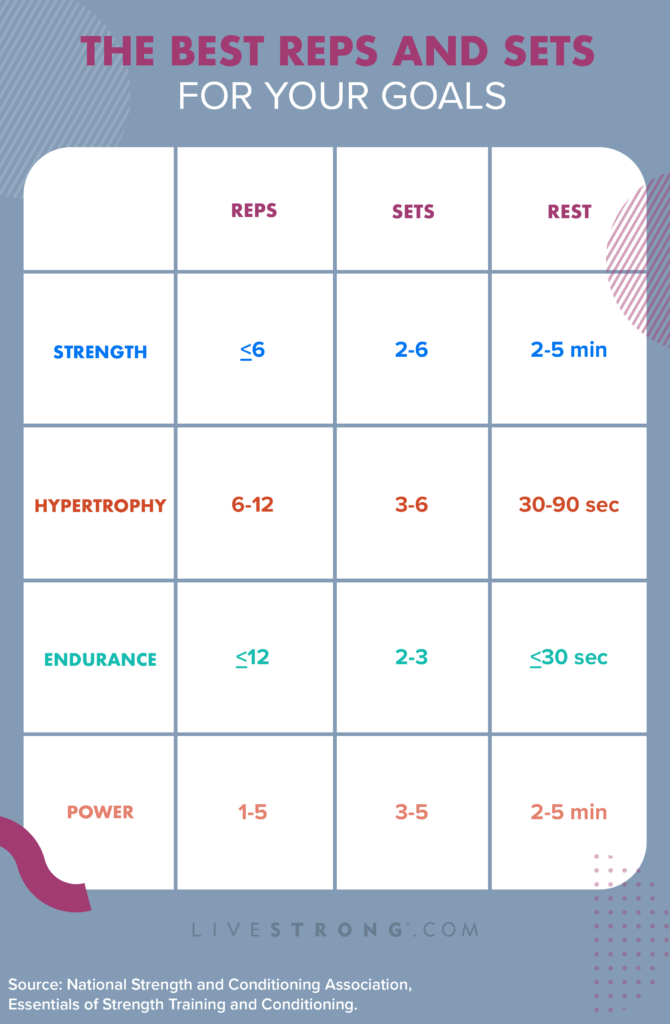
- Strength – 1-5 reps
- Hypertrophy – 8-12 reps
- Muscular endurance – 15-20+ reps
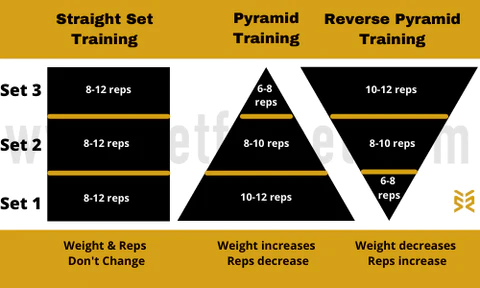
What are pyramids and reverse pyramids for reps?
Pyramid and reverse pyramid training refers to progressively increasing or decreasing the weight each set while reducing or adding reps:
Regular pyramid:
- Set 1: Light weight, higher reps
- Set 2: Add weight, reduce reps
- Set 3: Heavier weight, lower reps
- Set 4: Same as set 3 or drop one rep
Reverse pyramid:
- Set 1: Heavy weight, lower reps
- Set 2: Reduce weight, add reps
- Set 3: Lighter weight, higher reps
- Set 4: Same as set 3 or add one rep
This provides variety by hitting different rep ranges in one workout. It helps build strength, muscle, and endurance.
How many reps are good for building strength?
Lower rep ranges with heavier weights are best for developing raw strength:
- 1-5 reps per set build maximal strength
- 3-5 sets with 2-4 minute rests
- 75-90%+ of your 1 rep max weight
Lift heavy weights in the 1-5 rep range to build pure strength. This overloads the higher threshold muscle fibers through peak contraction. Ensure proper safety procedures.
What does rep failure mean?
Reaching muscular failure means you are unable to complete another full repetition with proper form. You have taken a set to the point where your muscles have fatigued to exhaustion.
Signs of failure:
- Inability to lift the weight through the full range of motion
- Form breakdown occurs
- Your spotter needs to assist you up
Training to failure places maximum mechanical tension on your muscles to spark growth. But avoid going to failure on all sets to manage fatigue.
What are drop sets and how do they use reps?
Drop sets involve reducing weight and immediately performing more reps with less rest:
- Lift heavy weight until failure at 6-8 reps
- Quickly lower weight by 10-20% without resting
- Pump out as many reps as possible until failure
- Repeat dropping the weight and churning out reps
This wrings every last bit of effort from your muscles by extending sets beyond normal capacity. But drop sets are extremely demanding, so use them sparingly!
What does rep tempo mean?
Rep tempo refers to the speed of each phase of the repetition:
- Eccentric/lowering phase
- Isometric contraction at bottom
- Concentric/lifting phase
- Isometric hold at top
Tempo is often denoted in seconds. For example:
- 4/0/2/0 = 4 seconds to lower, no hold, 2 seconds to lift, no hold
Slower tempos increase time under tension for the muscles. But don’t sacrifice good form by going too slow. Use a purposefully controlled tempo for best results.
What are cheat reps?
Cheat reps involve using momentum or assistance from other muscle groups to complete additional forced repetitions past the point of normal failure.
For example:
- Swinging weights up during biceps curls
- Arching the back or heaving the torso on bench press
- Bouncing out of the bottom position of squats
Cheat reps allow you to extend a set with poorer form after you have properly fatigued the target muscles. They can help spark new muscle growth. But do not make them a regular habit.
Can you build muscle with low reps and heavy weights?
Yes, lifting heavy weights for lower reps is an extremely effective way to build muscle mass:
- The mechanical tension stimulates muscle protein synthesis.
- It recruits higher threshold muscle fibers.
- More myofibrillar hypertrophy increases contractile proteins.
- Ramp up to a 3-5 rep maximum and add weight over time.
- Allow 2-4 minutes rest between sets.
- Use a controlled tempo without momentum.
Keep good form as the top priority over hitting higher weights for low reps. Let your muscles gradually adapt over time.
What are unilateral and bilateral exercises?
Unilateral exercises involve training one limb at a time such as:
- Single-arm dumbbell rows
- Single-leg hip thrusts
- Split squats
Bilateral exercises work two limbs simultaneously such as:
- Barbell bench press
- Regular squats
- Pullups
Unilateral moves better isolate each side while bilateral allows you to lift heavier weights overall. Incorporate both into your program.
Should you train to failure on all sets?
No, it is not recommended to take every set to absolute muscle failure:
- Occasional failure sets help break plateaus but cause significant fatigue.
- Avoid failure on compound exercises to maintain safety and form.
- Leave 1-2 reps “in the tank” on first sets to manage fatigue.
- Failure sets at the end of workouts help fully exhaust the muscle.
Strategically incorporate failure sets but don’t overdo it. Listen to your body and adjust as needed. Strength training requires balance.
What are compound sets?
Compound sets involve doing two or more exercises back-to-back targeting the same muscle group. This increases training volume and metabolic stress.
Example:
- Bench press: 10 reps
- Immediately into pushups: 10 reps
- 1 minute rest
- Repeat 3x
Compound sets boost conditioning and continually overload muscles within a workout for rapid gains. Use them strategically when looking to shock your body.
How do drop sets and intensity techniques use reps?
High intensity techniques like drop sets extend sets by reducing weight and continuing reps:
Drop Sets
- Lift heavy until failure at 6-8 reps
- Reduce weight by 10-20%
- Pump out more reps until failure
- Repeat drops
This forces extra reps beyond your normal limits to fully exhaust the muscle fibers.
Other techniques like supersets, rest-pause, and staggered sets also use reps in a strategic manner to increase intensity. Employ them carefully to avoid overtraining.
What does time under tension mean?
Time under tension refers to how long your muscles are strained during each set. This depends on:
- Number of reps
- Rep speed and tempo
- Use of advanced techniques like drop sets
More time under tension triggers greater muscle growth but also more fatigue. Ensure you balance tension with adequate rest and recovery between workouts.
What are burnout sets?
Burnout sets refer to a high rep set performed at the very end of a workout to fully exhaust the target muscle group. For example:
- Regular sets: 3 x 10-12 reps
- Burnout: 1 x 20-30 reps with 30 seconds rest between mini-sets
With lighter weight, you take reps beyond failure. This provides metabolic stress and sarcoplasmic hypertrophy to round out muscle growth. Utilize burnout sets periodically when looking to shock your muscles.
How can you build muscle with bodyweight reps?
To build muscle with bodyweight reps, focus on progressively overloading the muscles:
- Increase reps or total sets over time
- Use harder bodyweight progressions – regular vs. decline pushups
- How to Watch the Pittsburgh Steelers Play Tonight?
- Are Anaphora and Repetition the Same Thing?
- How To Check Ford F350 DEF Fluid Level?
- Can You Swim in Maumee Bay?
- How Does Gluttony Die in Fma Brotherhood?
- How to Connect to IHG WiFi on PS4?
- How Strong Is Gorr the God Butcher?
- Where Are Stryker Brigades Located?
- How to Get B Coins in Cats and Soup?
- When Did the Mayan Number System Start?
- How to Put Vinyl Siding on a Metal Mobile Home?
- What Is the Meaning of the Word Restrainer??
- Are Canned Yams Already Cooked?
- Where Are Blue Indigo Snakes From?